Does microscopic hematuria mean cancer? In fact, the overwhelming majority of patients who have microscopic hematuria do not have cancer. Irritation when urinating, urgency, frequency and a constant need to urinate may be symptoms a bladder cancer patient initially experiences.
What percentage of microscopic hematuria is cancer? In one study, only about 10 percent of people with visible hematuria and 2 to 5 percent of those with microscopic hematuria had bladder cancer [5,6]. Anyone with blood in their urine should be evaluated by a health care provider.
Should I be worried about microscopic hematuria? If you have no symptoms of microscopic hematuria, you may not know to alert your doctor. But if you do have symptoms, call your doctor right away. It is always important to find out the cause of blood in your urine.
What is the most common cause of microscopic hematuria? The most common causes of microscopic hematuria are urinary tract infection, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and urinary calculi. However, up to 5% of patients with asymptomatic microscopic hematuria are found to have a urinary tract malignancy.
Does microscopic hematuria mean cancer? – Related Questions
Does microscopic blood in urine always mean cancer?
Blood in the urine doesn’t always mean you have bladder cancer. More often it’s caused by other things like an infection, benign (not cancer) tumors, stones in the kidney or bladder, or other benign kidney diseases.
How to estimate field of view in microscope?
For instance, if your eyepiece reads 10X/22, and the magnification of your objective lens is 40. First, multiply 10 and 40 to get 400. Then divide 22 by 400 to get a FOV diameter of 0.055 millimeters.
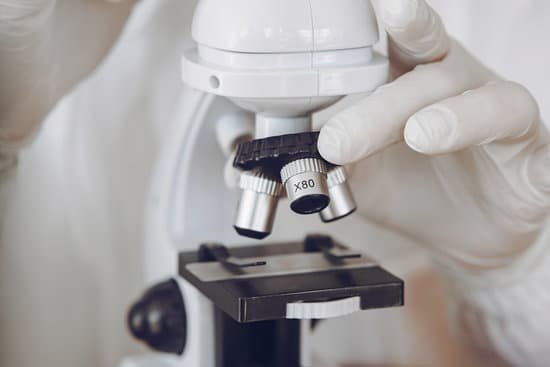
What do the numbers on microscope lenses mean?
Microscope objective lenses will often have four numbers engraved on the barrel in a 2×2 array. The upper left number is the magnification factor of the objective. For example, 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. The upper right number is the numerical aperture of the objective. For example 0.1, 0.25, 0.65, and 1.25.
What does the blue filter do on a microscope?
Daylight Blue Filter: The daylight blue microscope filter is for observation use only. It provides a pale gray-blue hue to the field of view and is often used to balance the light created by tungsten or halogen microscope lights to balance out the color of the microscopy light.
How to adjust contrast on a microscope?
To adjust the contrast in a bright light microscope, move the condenser so that it is as close to the stage as possible. Close the aperture all the way. Look through the eyepiece and check the contrast. Slowly open the aperture while continuing to view the specimen through the eyepiece.
Does microscopic colitis go away on its own?
Sometimes, microscopic colitis goes away on its own. If not, your doctor may suggest you take these steps: Avoid food, drinks or other things that could make symptoms worse, like caffeine, dairy, and fatty foods.
Why is cedar wood oil used in microscope?
In light microscopy, oil immersion is a technique used to increase the resolving power of a microscope. This is achieved by immersing both the objective lens and the specimen in a transparent oil of high refractive index, thereby increasing the numerical aperture of the objective lens.
Why can’t you see all organelles under a microscope?
However, most organelles are not clearly visible by light microscopy, and those that can be seen (such as the nucleus, mitochondria and Golgi) can’t be studied in detail because their size is close to the limit of resolution of the light microscope.
Why is a light microscope called a compound microscope?
The compound light microscope is a tool containing two lenses, which magnify, and a variety of knobs used to move and focus the specimen. Since it uses more than one lens, it is sometimes called the compound microscope in addition to being referred to as being a light microscope.
When to use iris diaphragm microscope?
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
What was the first microscope?
It’s not clear who invented the first microscope, but the Dutch spectacle maker Zacharias Janssen (b. 1585) is credited with making one of the earliest compound microscopes (ones that used two lenses) around 1600. The earliest microscopes could magnify an object up to 20 or 30 times its normal size.
What organelles can you see with a transmission electron microscope?
The cell wall, nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes are easily visible in this transmission electron micrograph.
What microscope is used to compare known and unknown impressions?
Comparison microscope is used to analyze the matching of the microscopic impressions found on the surface of bullets and casings.
Which lens is used in compound microscope?
Typically, a compound microscope is used for viewing samples at high magnification (40 – 1000x), which is achieved by the combined effect of two sets of lenses: the ocular lens (in the eyepiece) and the objective lenses (close to the sample).
What do you use a scanning electron microscope for?
Scanning electron microscopy can be used to identify problems with particle size or shape before products reach the consumer. Finally, industries that use small or microscopic components to create their products often use scanning electron microscopy to examine small components like fine filaments and thin films.
What does the word scope mean in microscope?
-scope- comes from Greek, where it has the meaning “see. ” This meaning is found in such words as: fluoroscope, gyroscope, horoscope, microscope, microscopic, periscope, radioscopy, spectroscope, stethoscope, telescope, telescopic.
When were transmission electron microscope invented?
Ernst Ruska at the University of Berlin, along with Max Knoll, combined these characteristics and built the first transmission electron microscope (TEM) in 1931, for which Ruska was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1986.
How a bright field microscope works?
In a standard bright field microscope, light travels from the source of illumination through the condenser, through the specimen, through the objective lens, and through the eyepiece to the eye of the observer. Light thus gets transmitted through the specimen and it appears against an illuminated background.
What is the microscopic gap between two neurons?
At a chemical synapse each ending, or terminal, of a nerve fibre (presynaptic fibre) swells to form a knoblike structure that is separated from the fibre of an adjacent neuron, called a postsynaptic fibre, by a microscopic space called the synaptic cleft. The typical synaptic cleft is about 0.02 micron wide.
Can high blood pressure cause microscopic blood in urine?
This is called microscopic hematuria. Hematuria is more common in an individual with large kidneys and high blood pressure. It is thought that the rupture of cysts or of the small blood vessels around cysts is the cause. Other causes could include kidney or bladder infection and kidney stones.
What organelles can only be seen with an electron microscope?
Mitochondria are visible with the light microscope but can’t be seen in detail. Ribosomes are only visible with the electron microscope.