What does the diaphragm do microscope? Opening and closing of the condenser aperture diaphragm controls the angle of the light cone reaching the specimen. The setting of the condenser’s aperture diaphragm, along with the aperture of the objective, determines the realized numerical aperture of the microscope system.
What is the diaphragm and why is it useful on the microscope? The microscope diaphragm, also known as the iris diaphragm, controls the amount and shape of the light that travels through the condenser lens and eventually passes through the specimen by expanding and contracting the diaphragm blades that resemble the iris of an eye.
How do you use a diaphragm on a microscope? Switch on your microscope’s light source and then adjust the diaphragm to the largest hole diameter, allowing the greatest amount of light through. If you have an iris diaphragm, slide the lever till the most light comes through. See the diagram below for help locating these parts.
What are two ways you can control the lighting of a compound microscope? It is possible to control the amount of light that shines through the slide by changing the size of the opening present in the stage. It is also possible to change the illumination by moving the mirror in microscopes that use one or by changing the brightness of the light source in the Illuminator.
What does the diaphragm do microscope? – Related Questions
How to calculate total magnification on microscope?
To figure the total magnification of an image that you are viewing through the microscope is really quite simple. To get the total magnification take the power of the objective (4X, 10X, 40x) and multiply by the power of the eyepiece, usually 10X.
Are demodex folliculorum mites microscopic?
folliculorum only becomes problematic if they exacerbate preexisting skin conditions, such as rosacea. There’s also increasing evidence that large amounts can cause skin problems. D. folliculorum is microscopic in size, so you won’t be able to diagnose its presence on your own.
What is working distance in regard to compound microscope?
Working distance is the distance between the front of the microscope objective lens and the surface of the specimen or slide coverslip at the point where the specimen is completely in focus.
Why can t ribosomes be seen with a light microscope?
Some cell parts, including ribosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, centrioles, and Golgi bodies, cannot be seen with light microscopes because these microscopes cannot achieve a magnification high enough to see these relatively tiny organelles.
What is used to cover microscopes?
Microscope slides are often used together with a cover slip or cover glass, a smaller and thinner sheet of glass that is placed over the specimen.
What a body tube on a microscope is used for?
The microscope body tube separates the objective and the eyepiece and assures continuous alignment of the optics. It is a standardized length, anthropometrically related to the distance between the height of a bench or tabletop (on which the microscope stands) and the position of the seated observer’s…
What organelles cannot be observed with a light microscope?
Some cell parts, including ribosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, centrioles, and Golgi bodies, cannot be seen with light microscopes because these microscopes cannot achieve a magnification high enough to see these relatively tiny organelles.
How to see chloroplasts under microscope?
Look at the leaf down a microscope and see if you can identify the small green chloroplasts. If you have difficulty seeing the chloroplasts, look at the cells at the edge where the leaf is very thin.
Do microscopic bugs live on normal skin?
Many microscopic bugs and bacteria live on our skin and within our various nooks and crannies. Almost anywhere on (or even within) the human body can be home to these enterprising bugs. Bugs affect us in a variety of ways: some bad, such as infections, but many good.
What is laboratory microscope?
The goal of any laboratory microscope is to produce clear, high-quality images, whether an optical microscope, which uses light to generate the image, a scanning or transmission electron microscope (using electrons), or a scanning probe microscope (using a probe).
Are all phytoplankton microscopic?
Derived from the Greek words phyto (plant) and plankton (made to wander or drift), phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that live in watery environments, both salty and fresh. … All phytoplankton photosynthesize, but some get additional energy by consuming other organisms.
How to adjust microscope condenser?
Most compound light microscopes have a small knob (2) to raise and lower the condenser holder. Lower this holder so the condenser can slide into the holder below the stage. Once you have inserted the condenser, tighten the set screw (3) to hold the condenser in place.
Can you clean microscope lenses with glasses cleaner?
Cleaning the internal optical surfaces or camera; if unexposed surfaces require cleaning, contact your microscope manufacturer. Optical spray cans containing pressurised liquid air, as these leave a small residue which is difficult to remove. Using window cleaners and glasses cleaners to clean your microscope lenses.
How to clean objective lens of microscope?
Place the objective lens on a dust-free surface. 2. Gently blow away loose dust that is on the surface of the optical glass with a dust blower, as if any dust left on throughout the cleaning process could scratch the optical glass or coating. Blow the air across the lens surface to avoid damaging it.
What kind of microscopes do pathologists use?
Although there are many different types of electron microscopes (e.g., high-voltage, scanning, analytic), the transmission electron microscope is most commonly used for diagnostic pathology (and is the type of electron microscope referred to throughout this chapter, unless otherwise noted).
Where is the inclination joint on a microscope?
A joint at which the arm is attached to the pillar of the microscope is called inclination joint. It is used for tilting the microscope.
What zoom microscope is needed to see blood cells?
At 400x magnification you will be able to see bacteria, blood cells and protozoans swimming around. At 1000x magnification you will be able to see these same items, but you will be able to see them even closer up.
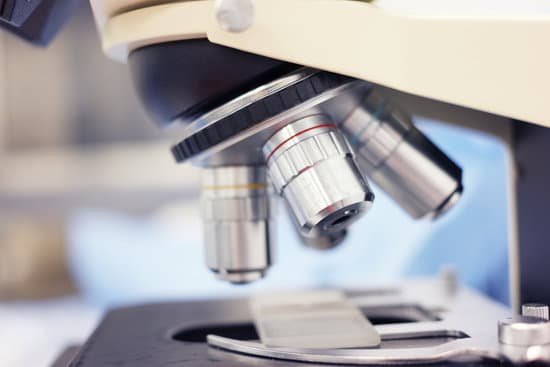
What is the meaning of revolving nosepiece in microscope?
Revolving Nosepiece or Turret: This is the part that holds two or more objective lenses and can be rotated to easily change power. Objective Lenses: Usually you will find 3 or 4 objective lenses on a microscope.
Who developed and improved the compound microscope?
A Dutch father-son team named Hans and Zacharias Janssen invented the first so-called compound microscope in the late 16th century when they discovered that, if they put a lens at the top and bottom of a tube and looked through it, objects on the other end became magnified.
How do you change magnification on a microscope?
On a standard stereo microscope (not a common main objective stereo microscope) the objective lens is built into the microscope and the only way to change this magnification is by adding an auxiliary lens to the existing objective lens. These are typically available in increments of 0.5x, 0.75x and 1.5x magnification.