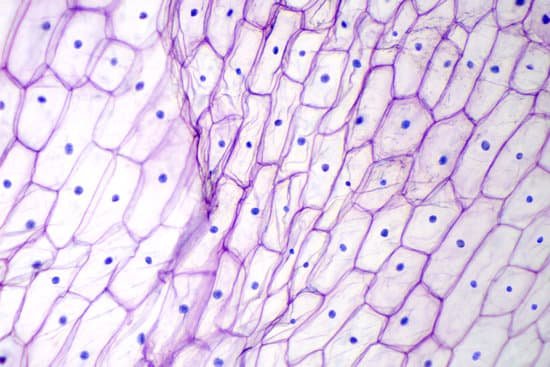
What can be observed with a transmission electron microscope? Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a technique used to observe the features of very small specimens. The technology uses an accelerated beam of electrons, which passes through a very thin specimen to enable a scientist the observe features such as structure and morphology.
What can you see with transmission electron microscope? The transmission electron microscope is used to view thin specimens (tissue sections, molecules, etc) through which electrons can pass generating a projection image. The TEM is analogous in many ways to the conventional (compound) light microscope.
What type of image would you see with a transmission electron microscope? Transmission electron microscopes (TEM) are microscopes that use a particle beam of electrons to visualize specimens and generate a highly-magnified image. TEMs can magnify objects up to 2 million times. In order to get a better idea of just how small that is, think of how small a cell is.
What can TEM measure? TEM is a well-known imaging technique that uses beam of electrons as seen in Fig. 5.7. … While TEM is used to measure the particle size of QDs, it can also provide information about the size distribution of the corresponding QD materials.
What can be observed with a transmission electron microscope? – Related Questions
What are the function of each part of microscope?
Eyepiece Lens: the lens at the top that you look through, usually 10x or 15x power. Tube: Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. Arm: Supports the tube and connects it to the base. Base: The bottom of the microscope, used for support.
What can you observe with a microscope?
A microscope is an instrument that is used to magnify small objects. Some microscopes can even be used to observe an object at the cellular level, allowing scientists to see the shape of a cell, its nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles.
How sem microscopes work?
The SEM is an instrument that produces a largely magnified image by using electrons instead of light to form an image. A beam of electrons is produced at the top of the microscope by an electron gun. … Once the beam hits the sample, electrons and X-rays are ejected from the sample.
What is a infrared microscope used to observe?
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms.
What does the microscope rests on?
Stage: The platform the slide rests on while being viewed. The stage has a hole in it to permit light to pass through both it and the specimen. The mechanical stage permits precise movement of the specimen.
What is the function of microscope arm?
Arm connects to the base and supports the microscope head. It is also used to carry the microscope.
Can we see atoms through microscope?
Atoms are really small. So small, in fact, that it’s impossible to see one with the naked eye, even with the most powerful of microscopes. … Now, a photograph shows a single atom floating in an electric field, and it’s large enough to see without any kind of microscope.
How far can compound microscopes measure?
Most measurements that are made with a compound microscope are between 0.2um to 25mm. It is hard to make measurements above 25mm becasue most eyepieces on a microscope do not have a field of view greater than 25mm.
What medicines can cause microscopic hematuria?
Drugs — Hematuria can be caused by medications, such as blood thinners, including heparin, warfarin (Coumadin) or aspirin-type medications, penicillins, sulfa-containing drugs and cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan).
What is a compound microscope function?
Typically, a compound microscope is used for viewing samples at high magnification (40 – 1000x), which is achieved by the combined effect of two sets of lenses: the ocular lens (in the eyepiece) and the objective lenses (close to the sample).
Why add oil to microscope objectives?
Placing a drop of oil with the same refractive index as glass between the cover slip and objective lens eliminates two refractive surfaces, so that magnifications of 1000x or greater can be achieved while still preserving good resolution.
What does microscope magnification numbers mean?
Microscope objective lenses will often have four numbers engraved on the barrel in a 2×2 array. The upper left number is the magnification factor of the objective. For example, 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x. The upper right number is the numerical aperture of the objective. For example 0.1, 0.25, 0.65, and 1.25.
What does an iris diaphragm do on a microscope?
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
How are microscopic examinations done?
Microscopic urinalysis is often done as part of an overall urinalysis. After a urine (pee) sample is collected, it’s put into a centrifuge — a special machine that separates the liquid in the urine from any solid components that may be present, such as blood cells, mineral crystals, or microorganisms.
Why can an electron microscope detect more detail?
Electrons have much a shorter wavelength than visible light, and this allows electron microscopes to produce higher-resolution images than standard light microscopes.
Which microscope is the most powerful?
Lawrence Berkeley National Labs just turned on a $27 million electron microscope. Its ability to make images to a resolution of half the width of a hydrogen atom makes it the most powerful microscope in the world.
What kind of microscope did robert hooke invent?
Interested in learning more about the microscopic world, scientist Robert Hooke improved the design of the existing compound microscope in 1665. His microscope used three lenses and a stage light, which illuminated and enlarged the specimens.
What is the function of inclination joint in compound microscope?
Inclination Joint: Where the microscope arm connects to the microscope base, there may be a pin. If so, you can place one hand on the base and with the other hand grab the arm and rotate it back. It will tilt your microscope back for more comfortable viewing.
What is the microscopic anatomy of a muscle cell?
Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a form of endoplasmic reticulum. Muscle fibers are composed of myofibrils which are composed of sarcomeres linked in series.
When was the light microscope first used?
In 1609, Galileo Galilei made a microscope by converting one of his telescopes. It had a diverging lens as an eyepiece and a converging lens as an objective. An early microscope made of two converging lenses was presented around 1620 by the astronomer Cornelius Drebbel.
How have microscopes contributed to our understanding of living organisms?
Microscopes allow humans to see cells that are too tiny to see with the naked eye. Therefore, once they were invented, a whole new microscopic world emerged for people to discover. … It allowed them to observe Eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles that perform different life functions.