What causes chronic microscopic hematuria? The most common causes of microscopic hematuria are urinary tract infection, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and urinary calculi. However, up to 5% of patients with asymptomatic microscopic hematuria are found to have a urinary tract malignancy.
Should I be worried about microscopic hematuria? If you have no symptoms of microscopic hematuria, you may not know to alert your doctor. But if you do have symptoms, call your doctor right away. It is always important to find out the cause of blood in your urine.
Can you have microscopic hematuria for years? ABSTRACT: Asymptomatic microscopic hematuria is an important clinical sign of urinary tract malignancy. Asymptomatic microscopic hematuria has been variably defined over the years. In addition, the evidence primarily is based on data from male patients.
What can cause microscopic blood in urine without infection? Microscopic urinary bleeding is a common symptom of glomerulonephritis, an inflammation of the kidneys’ filtering system. Glomerulonephritis may be part of a systemic disease, such as diabetes, or it can occur on its own.
What causes chronic microscopic hematuria? – Related Questions
What do capsules look like under microscope?
Capsules appear colourless with stained cells against dark background. Capsules are fragile and can be diminished, desiccated, distorted, or destroyed by heating. A drop of serum can be used during smearing to enhance the size of the capsule and make it more easily observed with a typical compound light microscope.
Which microscope achieves the highest magnification and greatest resolution?
The microscope that can achieve the highest magnification and greatest resolution is the electron microscope, which is an optical instrument that is designed to enable us to see microscopic details down to the atomic scale (check also atom microscopy).
How did the microscope influence cell theory?
The invention of the microscope led to the discovery of the cell by Hooke. While looking at cork, Hooke observed box-shaped structures, which he called “cells” as they reminded him of the cells, or rooms, in monasteries. This discovery led to the development of the classical cell theory.
What ordinary things look like under a microscope?
20 Ordinary Things That Look So Weird Under a Microscope They Seem to Belong to a Parallel Universe
What do euglena look like under a microscope?
When viewed under the light microscope, Euglena appear as elongated unicellular organisms that are rapidly moving across the field surface. … Although one flagellum is often seen, they have two flagella, one of which is often hidden in a part of the Euglena referred to as reservoir.
What does the high lens do on a microscope?
The high-powered objective lens (also called “high dry” lens) is ideal for observing fine details within a specimen sample. The total magnification of a high-power objective lens combined with a 10x eyepiece is equal to 400x magnification, giving you a very detailed picture of the specimen in your slide.
What does the diaphragm do on a compound microscope?
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
What does a pearl look like under a microscope?
Borrow a microscope or a powerful magnifying glass. Place your bead under the magnifying glass and examine its surface under a 64-power magnification loupe. Real pearls should look fine-grained, scaly, and labyrinth-like, while fake pearls should look grainy or mottled.
What cells can you see using a light microscope?
Explanation: You can see most bacteria and some organelles like mitochondria plus the human egg. You can not see the very smallest bacteria, viruses, macromolecules, ribosomes, proteins, and of course atoms.
Who built the compound microscope?
A Dutch father-son team named Hans and Zacharias Janssen invented the first so-called compound microscope in the late 16th century when they discovered that, if they put a lens at the top and bottom of a tube and looked through it, objects on the other end became magnified.
What should i use to clean my microscope lens?
Dip a lens wipe or cotton swab into distilled water and shake off any excess liquid. Then, wipe the lens using the spiral motion. This should remove all water-soluble dirt.
What is the pointer on a microscope?
A microscope pointer, also known as the eyepiece pointer, is a thin but sturdy piece of material built into or mounted onto a microscope’s eyepiece. … Its placement inside the eyepiece makes it part of the microscope’s lens assembly, and it isn’t affected by zoom magnification.
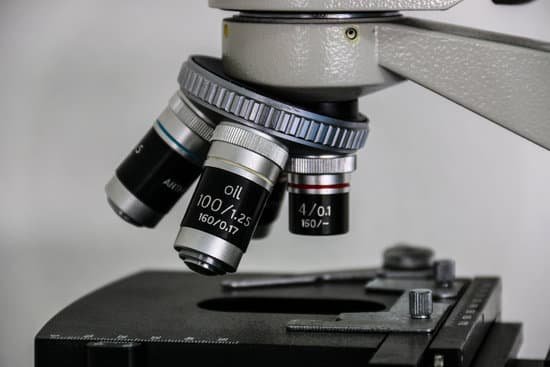
What are the powers of a microscope?
Most compound microscopes come with interchangeable lenses known as objective lenses. Objective lenses come in various magnification powers, with the most common being 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x, also known as scanning, low power, high power, and (typically) oil immersion objectives, respectively.
Are baby bed bugs microscopic?
Fully-grown bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed and dark brown or red in colour. A baby bed bug looks like a smaller version of the adult. Though tiny, they are usually visible to the naked eye, becoming bigger each time they molt.
Why is it important to calibrate your microscope?
Microscope Calibration can help ensure that the same sample, when assessed with different microscopes, will yield the same results. Even two identical microscopes can have slightly different magnification factors when not calibrated.
What does the low power objective do on a microscope?
Low power objectives cover a wide field of view and they are useful for examining large specimens or surveying many smaller specimens. This objective is useful for aligning the microscope. The power for the low objective is 10X. Place one of the prepared slides onto the stage of your microscope.
What is the highest magnification of a compound microscope?
Magnification. The actual power or magnification of a compound optical microscope is the product of the powers of the ocular (eyepiece) and the objective lens. The maximum normal magnifications of the ocular and objective are 10× and 100× respectively, giving a final magnification of 1,000×.
Which microscope moves a sharp probe?
A scanning probe microscope has a sharp probe tip on the end of a cantilever, which can scan the surface of the specimen. The tip moves back and forth in a very controlled manner and it is possible to move the probe atom by atom.
Is using microscope code for 63030 cpt coding?
First, CPT guidelines do not list 63030 as inclusive of the microscope so reporting 63030 and +69990 together is accurate per the AMA’s CPT coding rules.
Why can electron microscopes magnify smaller objects than optical microscopes?
The electrons are fired at the sample very fast. When electrons travel at speed they behave a bit like light, so we can use them to make an image. But because electrons have a smaller wavelength than visible light they can reveal very tiny details. This makes electron microscopes more powerful than light microscopes.
What is meant by microscopic dot?
A small Tamil village named ‘Kritam’, ‘probably the tiniest of the seven hundred thousand villages dotting the map of India’ is ‘indicated in the district survey map by a microscopic dot’. So, the small dot that is hardly visible in open eyes is the mark of a village on the map.